Local Dev with Render Workflows
Run tasks locally for faster development and testing.
Render Workflows is in public beta.
During the beta, bugs or changes in API/SDK behavior are possible as we continue refining the product. We welcome any and all feedback at workflows-feedback@render.com.
You can run workflow tasks on your local machine to iterate on them quickly. The Render CLI supports spinning up a local task server that simulates the entire run execution lifecycle. You can trigger task runs from your application code, or from the CLI itself.
As you iterate on your task definitions, the local task server picks up changes automatically. It also retains in-memory logs and results for each run (these are lost on server shutdown).
Prerequisites
Your development machine must have:
- The Render CLI version 2.12.0 or later
- A workflow project repo that defines and registers tasks
Starting the task server
From your workflow project repo, run the following command:
Replace <WORKFLOW_START_COMMAND> with the command to start your workflow service, such as:
Command not found?
- Make sure you've installed the Render CLI.
- Run
render --versionto confirm you're using version 2.12.0 or later.
Your local task server spins up and starts listening on port 8120.
You can specify a different port with the --port option:
Triggering local task runs
In application code
This section assumes you have an existing app that triggers task runs.
If you don't, first get set up with Triggering Task Runs.
You can configure your locally running apps to point to your local task server when triggering task runs. How you do this depends on whether your app uses the Render SDK or the Render API:
If your app uses the Render SDK (TypeScript or Python) to trigger task runs, set the following environment variable(s) to run tasks against your local task server:
If your app uses the Render API directly to run tasks, swap out the base URL you use for task-related endpoints with your local task server's URL.
Here's a Node.js example:
In this example, you would set the RENDER_TASKS_URL environment variable to your local task server URL (e.g., http://localhost:8120) to use it for development.
Note that the local task server only simulates task-related endpoints. Other Render API endpoints are not supported.
In the Render CLI
-
With your local task server running, run the following command:
Don't forget the
--localflag! Otherwise, the CLI lists tasks from your deployed workflow services.The CLI opens an interactive menu of your locally registered tasks:
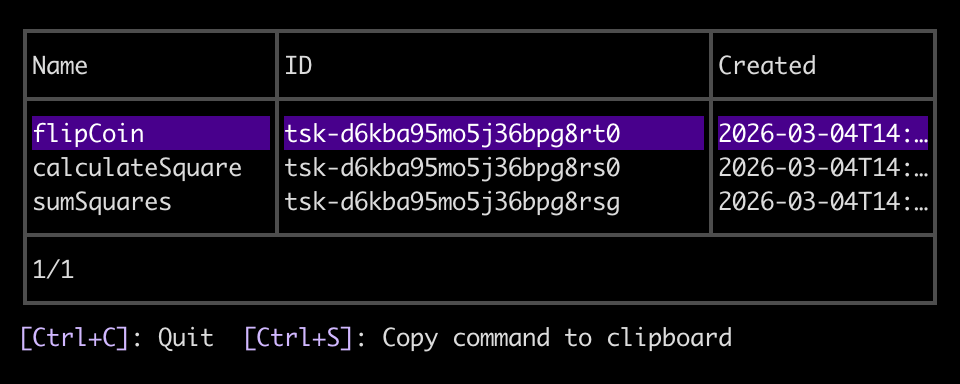
-
Select a task and press Enter, then select the
runcommand.The CLI prompts you to provide the task's input arguments as a JSON array:
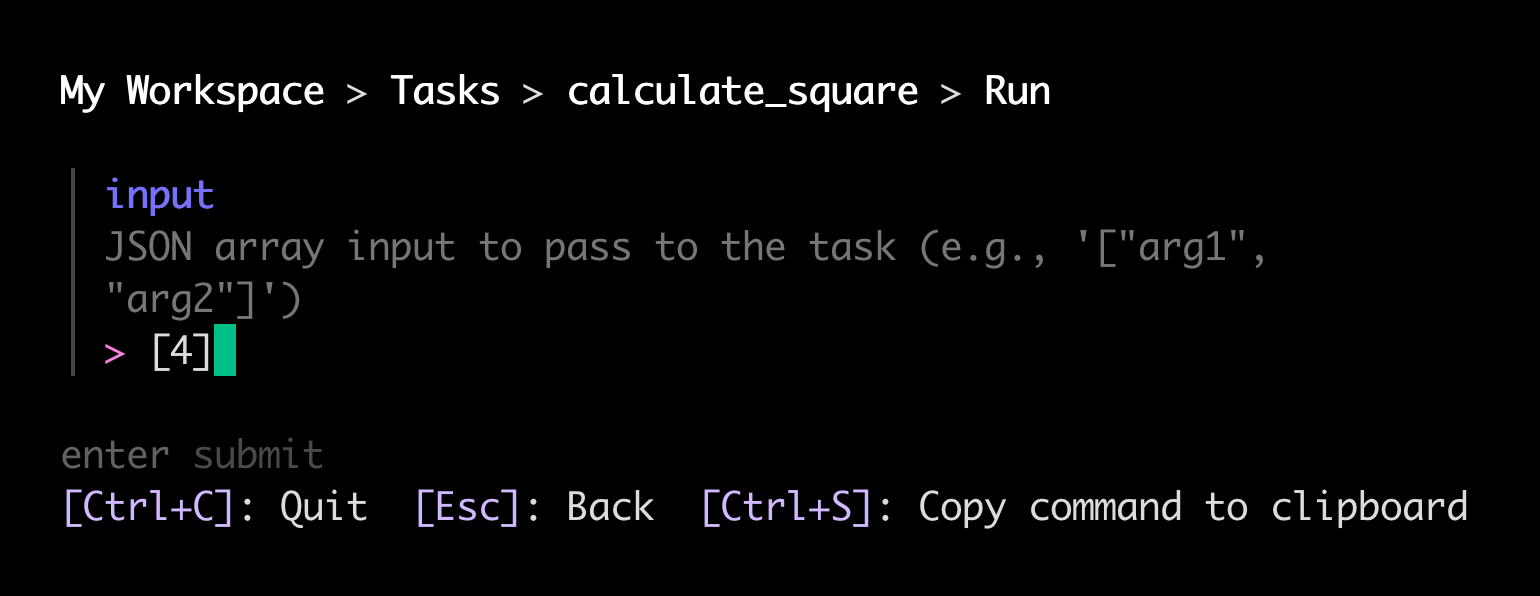
If your task takes zero arguments, provide an empty list,
[]. -
Provide your desired arguments and press Enter. The CLI kicks off your task with a request to your local task server and begins tailing its logs.
You can remain in this view to view live logs from your task run.
-
Press Esc to navigate back up to the list of commands for your task. This time select the
runscommand.The CLI opens an interactive menu of the task's local runs:
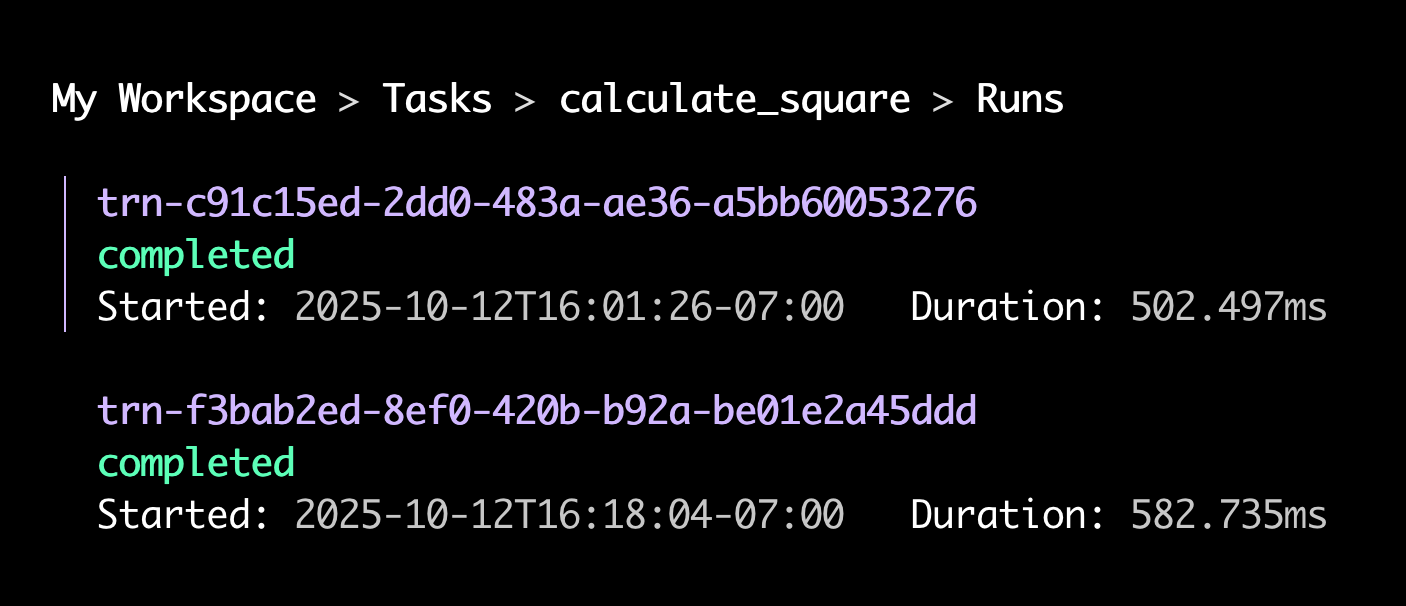
-
Select a run and press Enter, then select the
resultscommand.The CLI opens a view of the run's results:
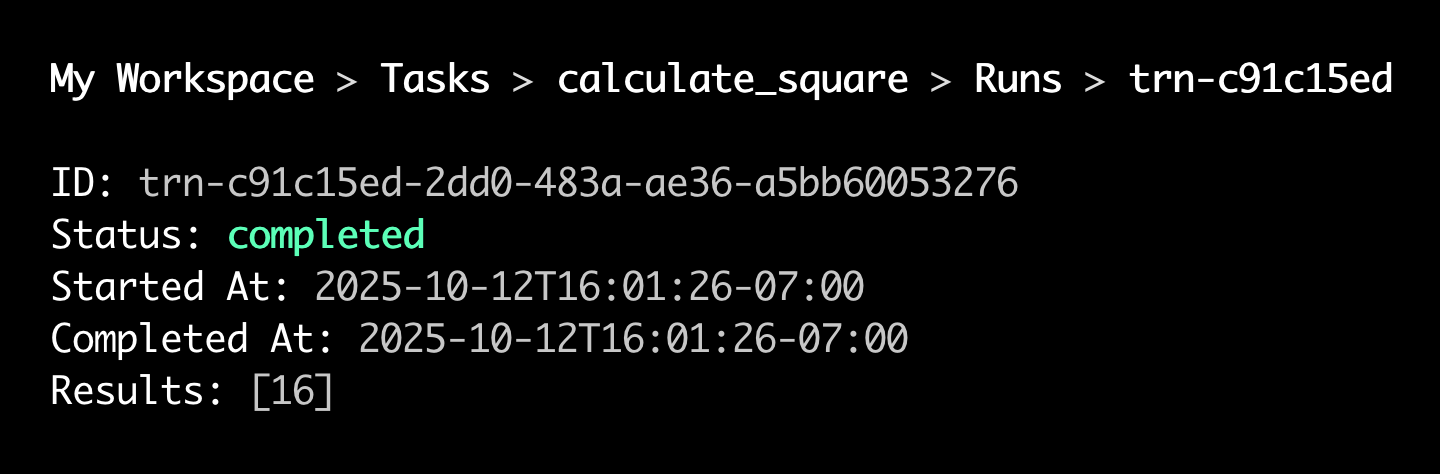
In non-interactive environments, provide any of -o text, -o json, or -o yaml to Render CLI commands to disable menu navigation and receive output in the desired format.
The example commands below use -o text:
-
With your local task server running, run the following command to list your locally registered tasks:
Don't forget the
--localflag for all of these commands! Otherwise, the CLI runs them against your deployed workflow services. -
Start a run for that task, passing input as a JSON array:
-
List runs for the task:
-
Fetch details and results for a run by its ID:
Local-only considerations
- Logs and results for local task runs are stored in memory by the local task server.
- This data is lost when the server shuts down.
- This data is retained indefinitely as long as the server is running. This can lead to high memory usage over time.
- If you trigger a high volume of local task runs, we recommend periodically restarting your local task server to free up memory.
- Identifiers for local tasks and runs are randomly generated IDs.
- The identifier for a given task differs each time you run the local task server.
- Local identifiers do not correspond to any values in your deployed workflow services.