Render Workflows
Rapidly spin up chains of long-running tasks on distributed compute.
Render Workflows is in public beta.
During the beta, bugs or changes in API/SDK behavior are possible as we continue refining the product. We welcome any and all feedback at workflows-feedback@render.com.
Use Render Workflows to rapidly distribute computational work across multiple independent instances:
Workflows are perfect for use cases that benefit from high-performance, distributed execution, such as AI agents, ETL pipelines, and data processing.
How it works
-
Using the Render SDK, you can mark functions in your code as tasks.
Here's minimal TypeScript for defining a task named
calculateSquare. First importtaskfrom the SDK, then call it with an options object and your task function:Here's minimal Python for defining a task named
calculate_square. First initialize aWorkflowsapp, then apply the@app.taskdecorator: -
In the Render Dashboard, you create a workflow service and link the repo containing your task definitions. Render automatically registers your defined tasks:
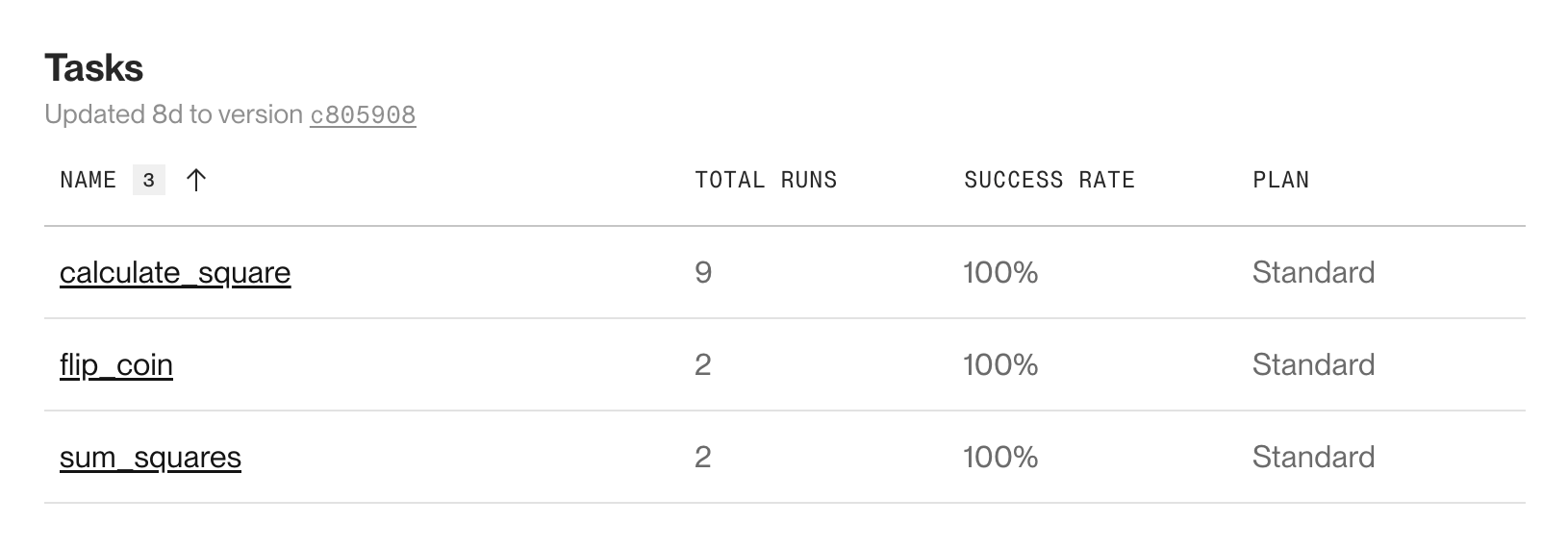
-
You can now trigger runs of your registered tasks from anywhere (web apps, agents, etc.) using the Render SDK or API.
Here's minimal TypeScript for triggering a run of
calculateSquareand passing the argument2:Here's minimal async Python for triggering a run of
calculate_squareand passing the argument2:Here's minimal synchronous Python for triggering a run of
calculate_squareand passing the argument2: -
Render spins up each triggered run in its own instance.
- This usually takes less than a second.
-
A run can trigger additional runs simply by calling the corresponding task function. This is called run chaining.
Below, the
sumSquarestask chains two parallel runs ofcalculateSquare:Below, the
sum_squarestask chains two parallel runs ofcalculate_square:
Runs execute alongside other Render service types, enabling fast and safe communication over your private network.
Core features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
|
Automatic queuing and orchestration |
Render coordinates the entire task run lifecycle for you, from queuing to spin-up to deprovisioning. |
|
Long-running execution |
Each task run can execute for up to 24 hours. |
|
Configurable retry logic |
Define retry behavior for each task in the event of a failed run, with exponential backoff. |
|
Configurable timeout |
Specify a timeout for runs of each task, from 30 seconds to 24 hours. |
|
Configurable compute specs |
Specify which instance type to use for runs of each task. |
|
Workflow-wide defaults |
Set the default retry logic, timeout, and instance type for all tasks in your workflow (and optionally override per task). |
|
Execution observability |
Track the progress and status of active and completed runs in the Render Dashboard. |
|
Outbound networking |
Runs can initiate network connections over both the public internet and your private network. Runs cannot receive incoming network connections. |
|
Unified SDK |
Install a single lightweight SDK both to register tasks and to trigger runs from your code. The Render SDK is currently available for TypeScript and Python. SDKs for additional languages are planned for future releases. |
Beta limitations
We'll address these limitations in future releases following beta:
- Workflows currently only support TypeScript and Python for defining tasks.
- SDKs for other languages are planned for future releases.
- Workflows do not provide built-in support for automatically triggering runs on a schedule.
- To schedule runs, you can create a cron job that runs your tasks on the desired schedule.
- If a workflow belongs to a network-isolated environment, its runs cannot communicate with other services in that environment over its private network.
- Workflows do not yet support running tasks on HIPAA-compliant hosts.
- To prevent accidental PHI exposure, it is not currently possible to create new workflows in a HIPAA-enabled workspace.
- If you enable HIPAA compliance for a workspace that already has workflows, do not process PHI in your workflows.
Get started
Now that you know the basics, you're ready to create your first workflow!
Billing
See Limits and Pricing for Render Workflows.
FAQ
How do I get started with Render Workflows?
Get started with Your First Workflow.
Which languages can I use to define workflow tasks?
The Render SDK is available for TypeScript and Python.
SDKs for additional languages are planned for future releases.
Can I trigger task runs without using the Render SDK?
Yes. For languages without Render SDK support, you can trigger runs by calling the Render API directly.
For details, see Triggering Task Runs.
Can my task runs receive incoming network connections?
No. Similar to background workers, task runs must initiate any required network connections.