Edge Caching for Web Services
Serve static content from a global edge cache for faster delivery.
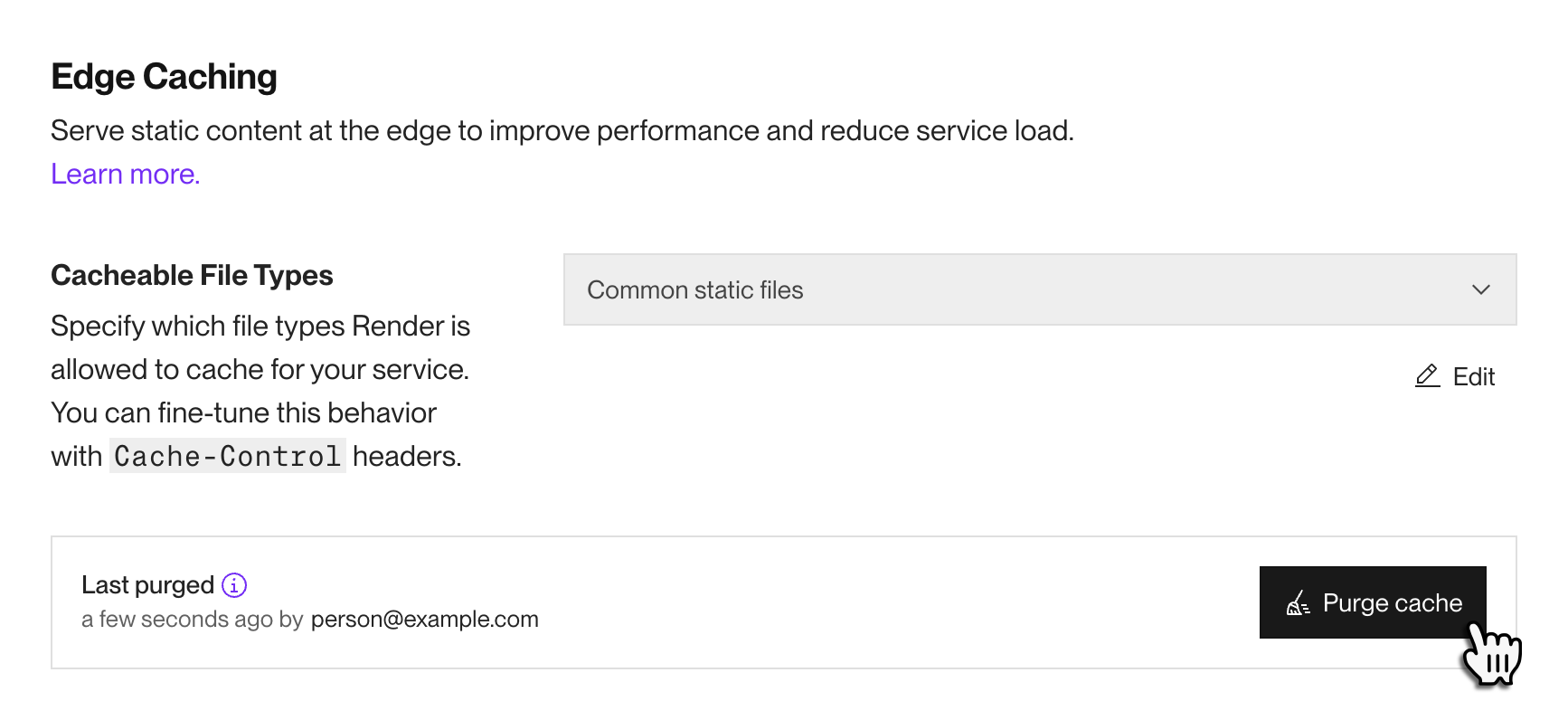
Render provides edge caching for static assets (documents, images, etc.) served by paid web services. With edge caching enabled, you can speed up response times and reduce load on your web service:
Edge caching is powered by the same global CDN as Render static sites.
Setup
Edge caching is not available for free web services.
-
In the Render Dashboard, open your web service's Settings page and scroll down to the Edge Caching section:
-
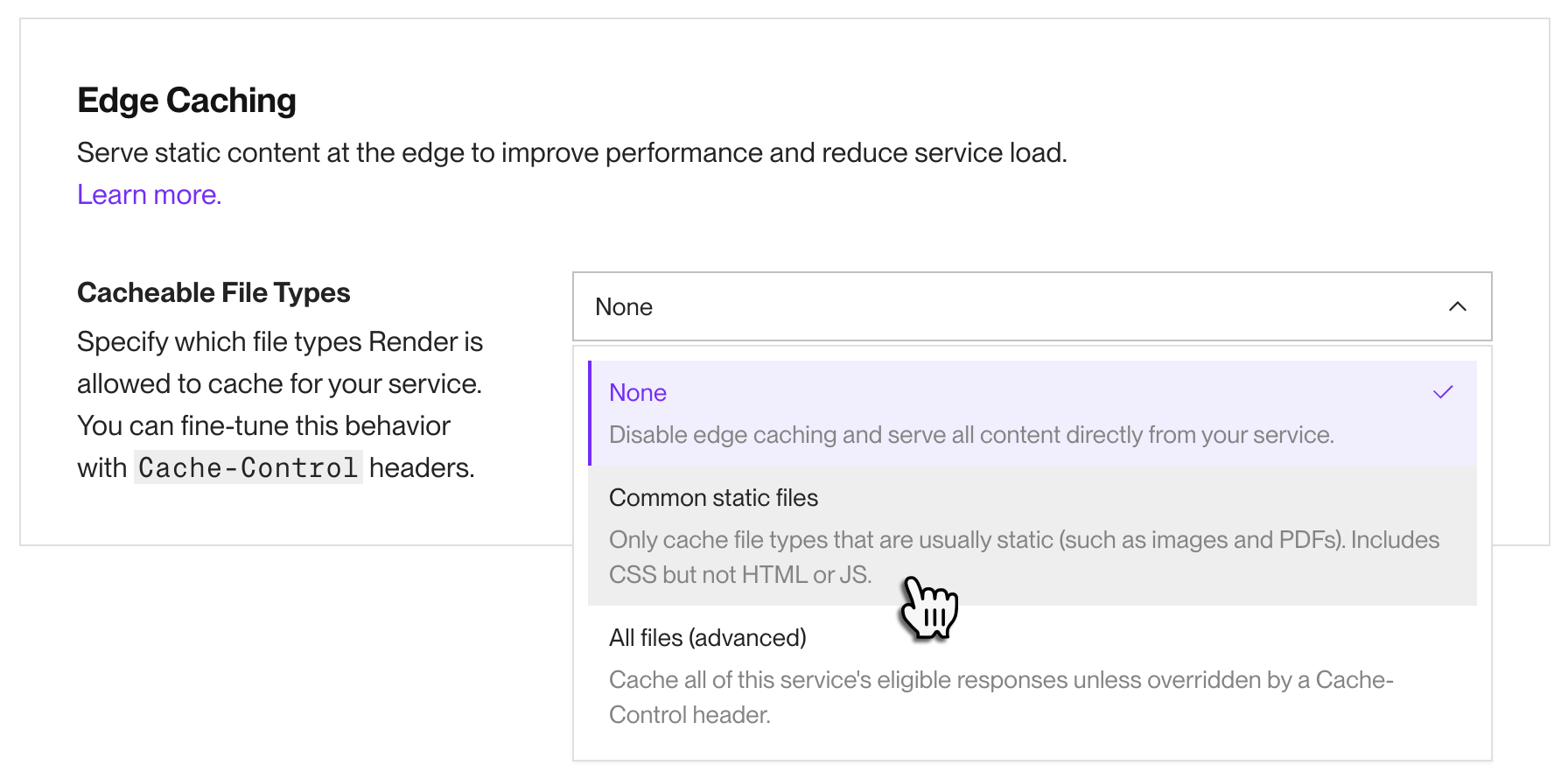
Under Cacheable file types, click the dropdown and select an option:
Option Description None
Disables edge caching. All assets are served from your web service.
This is the default option.
Common static files
Unless overridden by a
Cache-Controlheader, Render caches assets with the following file types:7zaviavifbinbmpbz2classcsscsvdmgdocdocxeotejsepsexeflacgifgzicoisojarjpegjpgjsmidmidimkvmp3mp4oggotfpdfpictplspngpptpptxpsrarsvgsvgzswftartiftiffttfwebmwebpwoffwoff2xlsxlsxzipzstOther file types are never cached, regardless of
Cache-Controlheaders.All files
Unless overridden by a
Cache-Controlheader, all of your service's eligible responses are cached, regardless of file type. This might include dynamic content.If you use this option, make sure to set
Cache-Controlheaders for dynamically generated content to prevent it from being cached. Otherwise, you might serve the wrong version of that content to clients. -
After you select an option, a confirmation dialog appears. Review and Confirm the notices, then click Save changes.
You're all set! Render begins caching your web service's cache-eligible responses.
How edge caching works
Whenever a client sends an HTTP request to your cache-enabled web service, Render determines whether the request is eligible to serve from the edge cache. (For details, see Cache eligibility.)
If the request is cache-eligible, Render checks the edge cache for the corresponding resource.
-
If the requested resource is in the cache (and the entry isn't stale), Render serves the cached version:
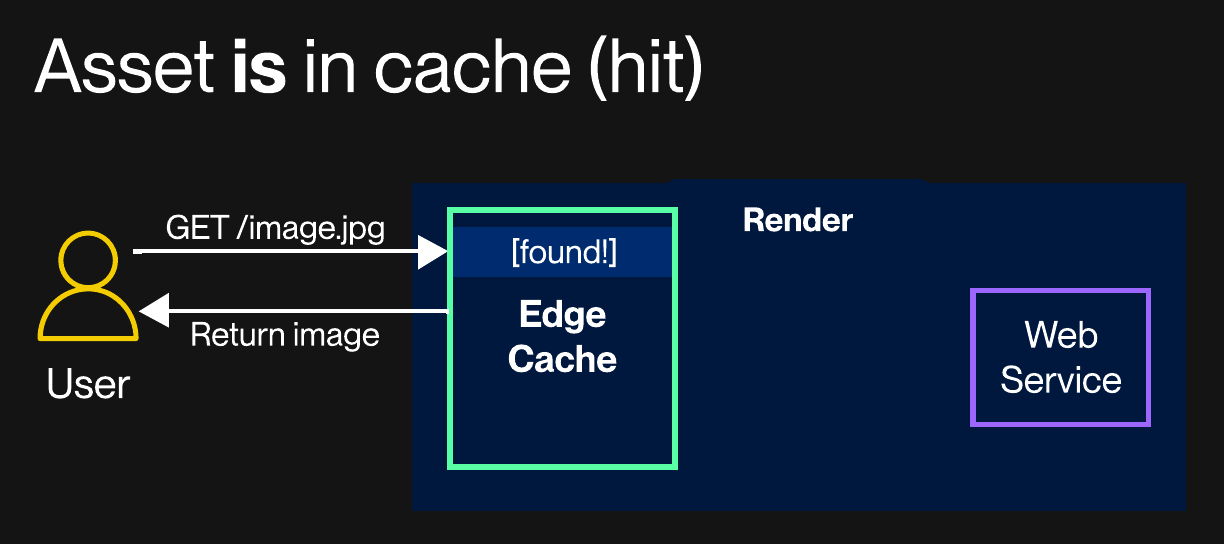
In this case, the request never reaches your web service. This speeds up the response and reduces load.
-
Otherwise, Render fetches the resource from your web service and—if it's also cache-eligible—caches it for future requests:
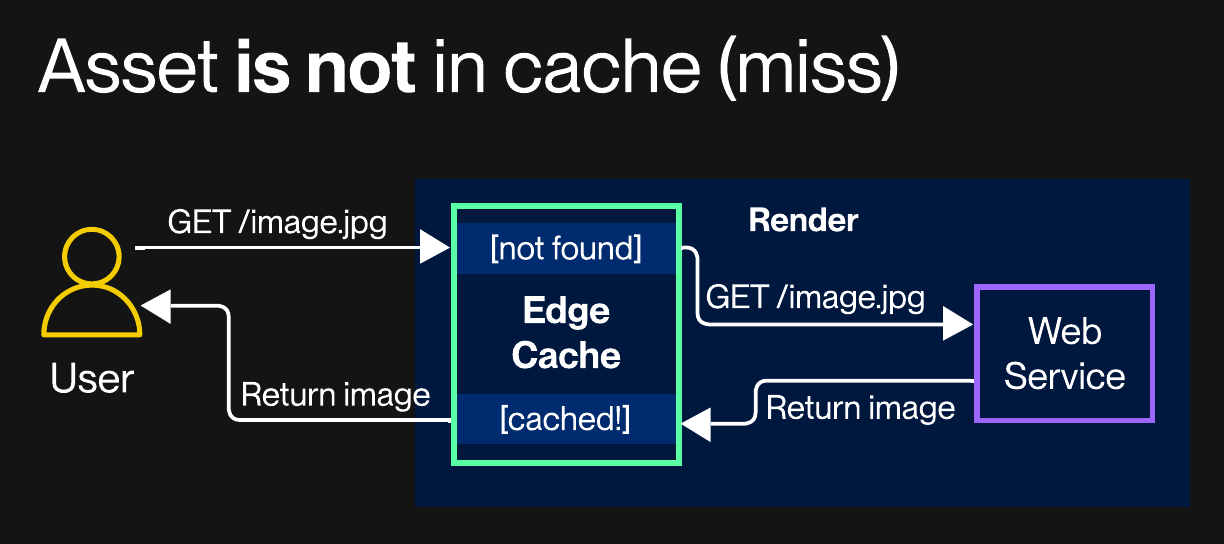
Cache eligibility
When serving a request from your web service, Render uses the following logic to determine whether the response can be cached for future requests:
* See details below.
To summarize, all of the following must be true for a response to be cache-eligible:
- The originating request must use the
GETorHEADHTTP method. - The requested resource must have a cacheable file type based on your settings.
- The response must either include a
Cache-Controlheader that allows caching or have a default-cacheable status code. - Additionally, the response must not include a
Set-Cookieheader.
Cacheable file types
When you enable edge caching for your web service, you select one of the following options for Cacheable file types:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
Common static files |
Unless overridden by a
Other file types are never cached, regardless of |
|
All files |
Unless overridden by a If you use this option, make sure to set |
Default-cacheable status codes
If your web service returns a cache-eligible response without a Cache-Control header, Render caches the response if it has one of the following status codes (and applies the corresponding default TTL):
| Status code | Default TTL |
|---|---|
| 200, 206, 301 | 120 minutes |
| 302, 303 | 20 minutes |
| 404, 410 | 3 minutes |
Invalidation and expiration
To help ensure that clients receive up-to-date content, Render invalidates edge cache entries in the following scenarios:
| Scenario | Description |
|---|---|
|
New deploys |
Each time you successfully deploy a new version of your web service, Render purges all of the service's edge cache entries. This way, the cache doesn't serve stale content from the service's previous version. Render waits until all of the previous version's instances have shut down before purging the cache (learn more about zero-downtime deploys). Failed deploys do not trigger a purge. Purging the cache might briefly increase your web service's request volume, but only slightly. See details. |
|
TTL expiration |
Each cache entry has a corresponding time-to-live (TTL). When an entry's TTL expires, the entry is considered stale. The next request for a stale entry is sent to your web service, which refreshes the entry. |
|
Manual purge |
You can trigger a cache purge for your web service from its Settings page in the Render Dashboard:
As with a new deploy, this purges all of your web service's associated edge cache entries. Purging the cache might briefly increase your web service's request volume, but only slightly. See details. |
Load protection on cache purge
Whenever you purge your web service's edge cache (either manually or by triggering a new deploy), Render's CDN automatically protects your web service from receiving a sudden influx of requests.
If multiple clients request the same uncached resource, Render's CDN forwards only one of those requests along to your web service. The CDN caches your web service's response, then serves it to all waiting clients. This pattern is called request collapsing.
Your web service might experience a brief traffic increase after a cache purge, but thanks to request collapsing, the size of that increase is roughly equal to the number of unique resources being requested. This is usually a small fraction of your service's total request volume.
Setting Cache-Control headers
You can customize Render's edge caching behavior for a particular resource by including a Cache-Control (or CDN-Cache-Control) header in your web service's response:
New to cache control headers?
Learn more about supported response directives.
| Customization | Description |
|---|---|
|
Set a TTL (time-to-live) |
Do both of the following in your response's
|
|
Disable caching |
Do either of the following in your response's
|
|
Set revalidation behavior |
Include a combination of the |
Precedence rules
Render applies the following precedence rules to cache control headers:
- The
CDN-Cache-Controlheader takes precedence over theCache-Controlheader if both are present. - The
s-maxagedirective takes precedence over themax-agedirective if both are present.
Inspecting cache behavior
Each response from a cache-enabled web service includes a CF-Cache-Status header:
The value of this header indicates whether the response interacted with the edge cache and in what way. The most common values are:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The response was served from the edge cache. |
|
|
The response was not found in the edge cache. It was served from your web service and cached if eligible. |
|
|
Some element of the incoming HTTP request was not cache-eligible, and the response was served from your web service. Most commonly indicates one of the following:
|
|
|
The response was found in the edge cache, but its TTL had expired. It was served from your web service and the edge cache was updated with the new response. |
|
|
The response was served directly from your web service and was not stored in the edge cache, usually for one of the following reasons:
|